January Business Conditions Monthly
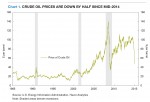
Crude oil prices have fallen by about half since mid-year (Chart 1). We see three key drivers responsible for the decline. First, Saudi Arabia’s decision to protect its share of the global market rather than managing prices, as it has in the past. Second, global economic growth has yet to fully recover from the financial crisis, reducing demand growth. Third, high oil prices in the pre-crisis years set the foundation for a surge in output among high-cost producers including the U.S.
Together, these three developments contributed to significant changes in the global supply and demand balance of the global crude market. Throughout this report, we look at the effects of lower oil prices, identifying the positive and negative impacts.